Takt time, cycle time and lead time. Do you know what these times mean and why should you be interested in them? It’s the pace, the turnaround and the delay. These are key elements of productivity.

These concepts are clear and easy to understand in the manufacturing sector because the products are visible. In the services, they are more abstract. Nevertheless, their mastery improves the performance and therefore the results of your organization.
Takt time or pace
The takt time is the pace of customer demand. It is calculated over the shortest possible period, in the idea of just in time.
- In the automotive sector, using the number of vehicles sold per day (500 for example), a plant can calculate the production rate required to meet the demand. If the workers produce for 12 hours a day, then you have to produce almost 42 cars an hour, or one car every 86 seconds, that’s the pace!
- For a hairdresser, it will be measured in a number of customers who request a service every hour, for example.
- For a fiber optic connection, the rate is measured in a similar way: the number of customers to be connected and serviced each week divided by the available time volume. For example, if a regional business needs to visit 150 clients per week, with two teams working 40 hours per week, then the rate is 32 minutes per client.
Pace seasonality
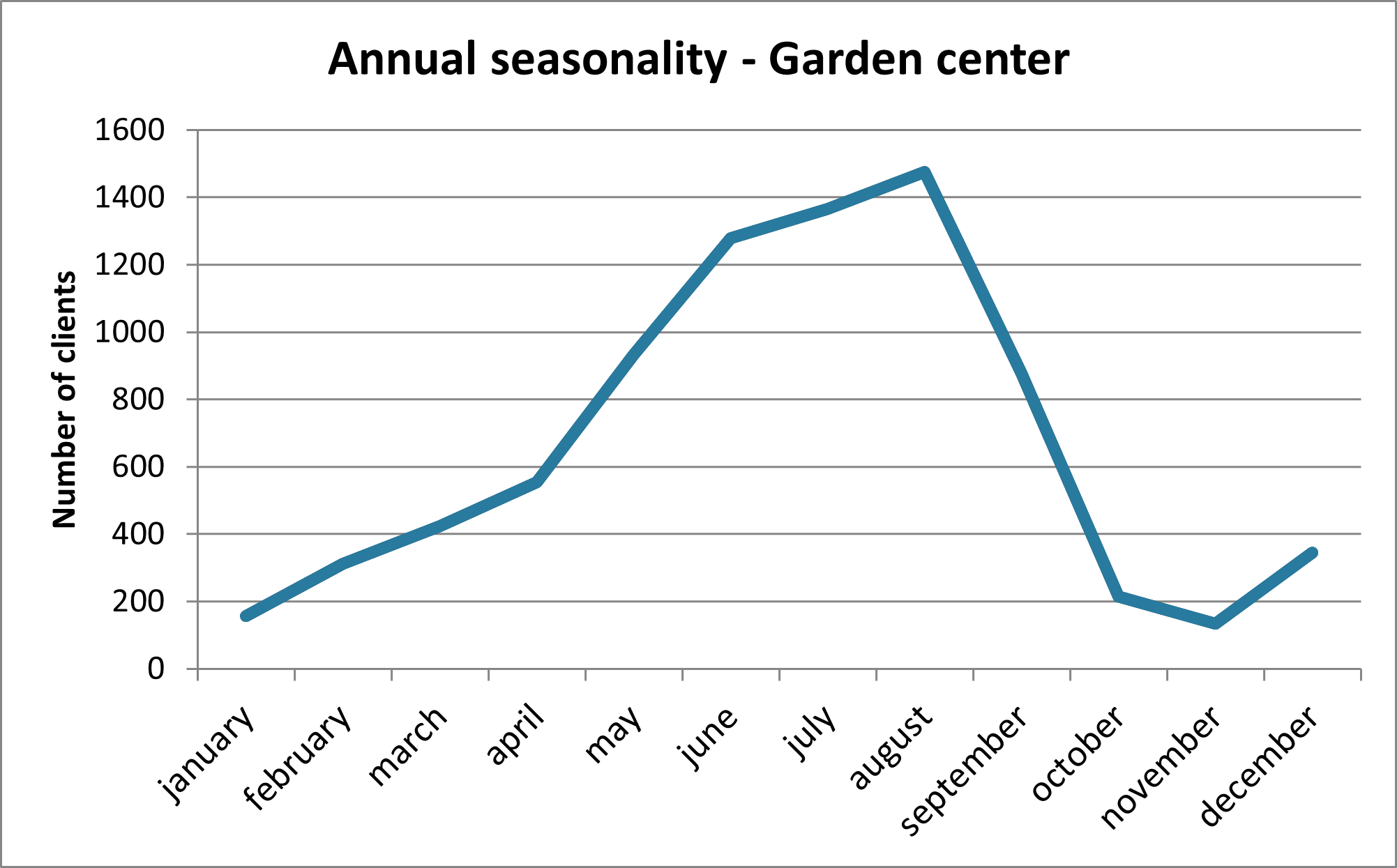
The rate of customer demand can encounter two types of seasonality: within the day and during the year.
During the year, weather, seasons, school holidays, paydays, can influence the goodwill. Think of shops, a bike shop, a hotel on a beach or a ski resort. Seasonality can also be repeated every week. For example, Monday may be the busiest day for an on line business because it processes orders placed over the weekend.
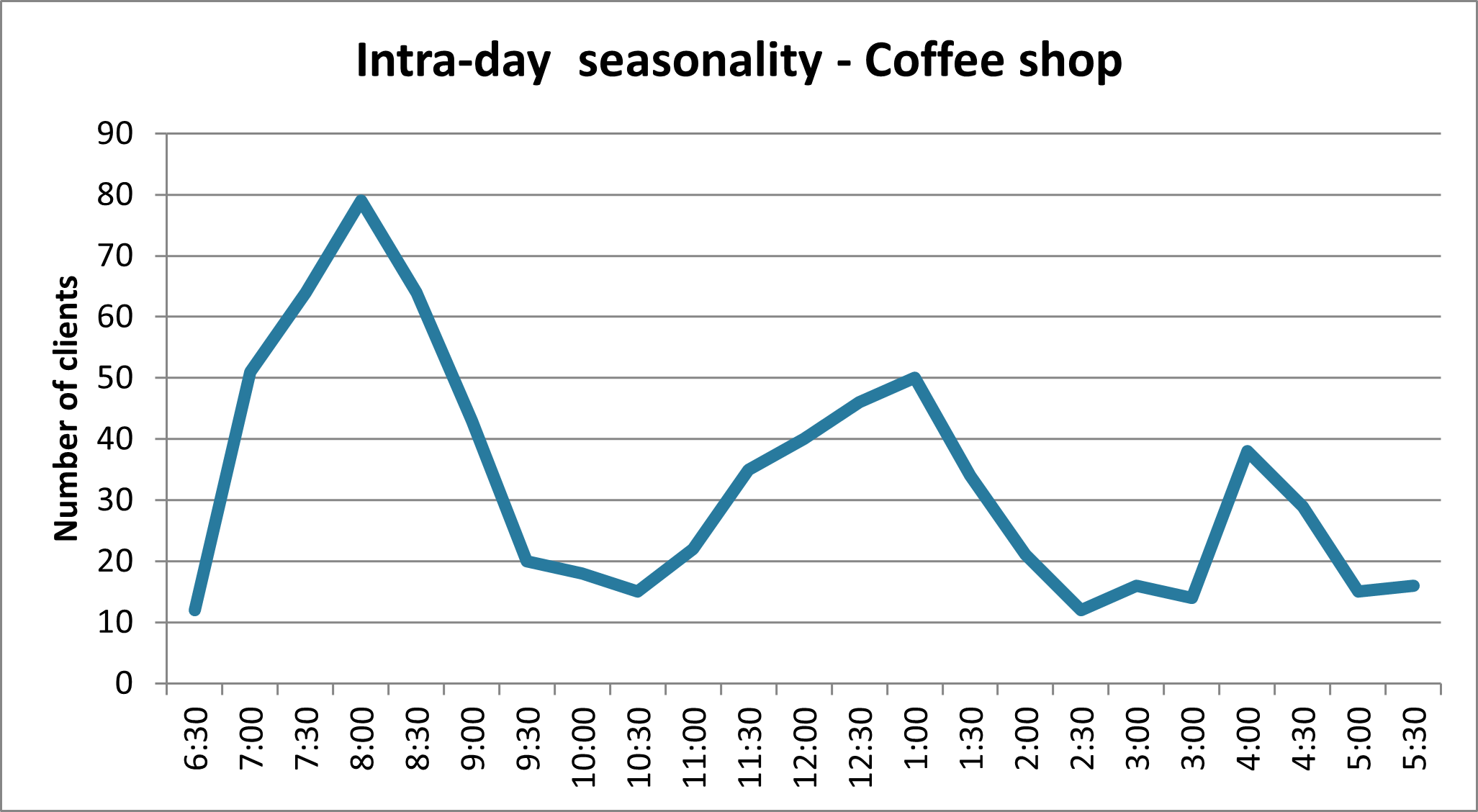
There is also an intra-day seasonality: during the same day, traffic may also vary depending on the service you offer: a restaurant sees a peak of activity between 11:30 and 2 pm for example, or a medical secretary has a peak of activity in the morning, when patients call to see a doctor.
Cycle time
The cycle time is the time required to produce the products or services. It is measured by calculating the time between the first and last step of the operation.
- In the automotive sector, a semi-automated production line can produce one car every five minutes, which is the standard cycle time for this production line.
- The hairdresser takes 30 minutes to cut the hair of a client, from the laying of the cloak, until the payment.
- The fiber connection team requires 60 minutes to complete its work, including travel time to the customer’s location.
- The restaurant can serve its customers in one hour (from the customer’s order until payment)
- For a doctor the time required to diagnose a patient and prescribe care is 15 minutes.
- The secretary needs 4 minutes to take a patient appointment.
When you compare the cycle time with the throughput, you immediately identify problems. My fiber connection company is going to have a long waiting list soon. The automotive plant will have to switch to 3-shift operation to meet the demand.
Lead time or delay
This is the time between the order and the delivery of the product or service. Some people measure it only in the organization. For me, it obviously starts with the customer. If you are able to deliver in 3 days, but the customer waits 10 days for the order to start being processed, the total delay is 13 days, not 3 days…
In some cases, the delay is equivalent to the cycle time, when all steps are synchronized, but this is quite rare. Here are some examples:
- In the automotive sector this time varies from two weeks to several months. It is measured by calculating the delay between the order by the customer and the delivery of his vehicle.
- For the fiber optic connection company, the delay is calculated between the customer’s request and the activation of the connection.
- In the restaurant, this is the time between arrival at the restaurant and departure.
- Same for a medical appointment. The delay includes the time of registration with the secretariat, as well as the possible delay of the doctor …
Customers expect to have the shortest lead time possible. The organization needs to find ways to reduce it as it runs the risk that the customer will change their mind in the meantime. Here are some techniques to reduce these different times, and therefore be more efficient!
